
Key Takeaways
- Scalable pipeline generation in B2B SaaS depends on integrated tracking, clear ICP definition, and disciplined channel focus, not isolated campaigns.
- Google Ads, LinkedIn, and retargeting work best when each channel has a defined role in capturing and progressing high-intent demand.
- Landing pages, lead nurturing, and measurement need tight alignment so teams optimize toward Net New ARR and payback instead of vanity metrics.
- Scaling comes from performance-based decisions, realistic CAC and payback targets, and gradual expansion into ABM, partners, and new channels.
- SaaS teams that want an experienced partner for this full system can work with SaaSHero, and can schedule a discovery call to get a tailored roadmap.

Prerequisites and Context
Effective pipeline generation needs the right tools, access, and baseline data before campaigns launch.
- Tools: CRM such as HubSpot, Salesforce, or Pipedrive, marketing automation, web analytics, and paid ad accounts on Google Ads and LinkedIn, plus landing page capabilities with Webflow, Unbounce, or your CMS.
- Data access: Admin access to your site, CRM, and ad accounts, with recent data on CAC, LTV, and basic conversion rates.
- Business context: Clear ICP, average sales cycle, main acquisition channels, and understanding of MRR, CAC, and churn.
- Time: Plan 4–6 weeks for initial setup and 10–15 hours per week early on, then 5–10 hours per week for optimization.
- Budget: Expect at least $5,000–$10,000 per month in ad spend plus tools and any agency or contractor support.
Pipeline Framework Overview
Scalable pipeline generation for SaaS usually follows six connected steps that share data and feedback.
- Step 1: Multi-channel foundation setup to connect tracking, analytics, and CRM.
- Step 2: High-intent channel activation on Google Ads and LinkedIn.
- Step 3: Conversion-focused landing pages and ongoing testing.
- Step 4: Lead nurturing, scoring, and sales handoff.
- Step 5: Revenue-focused measurement and attribution.
- Step 6: Scaling and optimization based on payback and pipeline data.
Step 1: Multi-Channel Foundation Setup
Start with infrastructure that ties every meaningful interaction back to opportunities and revenue.
Modern B2B SaaS teams map each ad platform to a role in the evaluation cycle. Google Ads captures in-market demand, LinkedIn creates and warms demand in target accounts, and retargeting reinforces messages for visitors who did not convert.
Key actions include:
- Install tracking: Add Google Analytics, Google Ads conversions with offline imports, and LinkedIn Insight Tag across key pages, and connect them to your CRM.
- Standardize UTMs: Use clear values for source, medium, campaign, and content so every click is traceable to pipeline.
- Test data flow: Complete test conversions from each channel and confirm they appear correctly in analytics and CRM, including original source on closed-won deals.
Step 2: High-Intent Channel Activation
Focus early budget on buyers already researching solutions and competitors.
Paid search tends to convert best for solution-aware and competitor-aware queries such as “tool alternative” or “X vs Y”. Launch tightly themed Google Ads search campaigns around competitor names, solution terms, and core problem phrases from your ICP.
For competitor conquesting, create separate ad groups per competitor with terms like “[competitor] pricing” and send traffic to focused comparison pages that address switching reasons.
LinkedIn Ads help reach specific roles and companies inside your ICP. Use Sponsored Content and Message Ads aimed at defined titles, industries, and company sizes that match your best customers.
Budget guidance:
- Allocate about 60 percent to Google search and 40 percent to LinkedIn at the start, then rebalance based on CAC and pipeline.
- Prioritize Google Ads if ACV is under $500 per month, and prioritize LinkedIn for higher ACV or enterprise motions where precision targeting matters more than click cost.
Step 3: Conversion Optimization Engine
Dedicated landing pages that match buyer intent create higher conversion rates and better-qualified pipeline.
Comparison and solution-focused pages that show clear value, proof, and a direct CTA above the fold usually beat generic pages. Build separate pages for competitor comparisons, core features, and key problems.
Each landing page should include:
- A clear headline that states who the product is for and the main outcome.
- Short benefit copy, social proof such as logos or testimonials, and a primary call to action like demo or trial.
- Simple forms with only essential fields for early-stage startups, and additional qualification fields for enterprise-focused teams.
- Mobile-friendly layouts, since research often begins on mobile even if deals close on desktop.
Set up basic A/B tests on headlines, CTAs, form length, and social proof placement, and keep tests focused on one major variable at a time.
Step 4: Lead Nurturing and Qualification
Consistent follow-up turns early interest into qualified opportunities across long B2B sales cycles.
Tools such as ActiveCampaign enable behavioral nurturing that aligns with down-funnel events like activation and revenue. Build sequences for new leads, product education, and re-engagement, and map each to clear next steps.
Support these flows with:
- Content that speaks to objections, use cases, ROI, and implementation, including case studies and comparison guides.
- Lead scoring that combines fit data such as role and company size with engagement data such as visits and email activity.
- Defined rules for when a lead becomes an MQL and SQL, plus a standard handoff package for sales that includes source and history.
- Retargeting audiences on platforms like Meta that focus on visitors to high-intent pages and engaged contacts to recapture demand efficiently.
Step 5: Performance Measurement and Attribution
Teams that scale reliably connect spend to opportunities, ARR, and payback instead of form fills alone.
Attribution platforms link ad spend to closed-won revenue so optimization can move toward pipeline and ARR. Configure CRM fields to preserve first-touch and key milestones, then tie them to opportunity and deal records.
Focus on metrics such as:
- Net New ARR and pipeline generated by channel.
- Blended CAC and payback period, with a target of 12 months or less for most SaaS startups when evaluating channels.
- SQL volume, close rates, and sales cycle length by source.
Unified reporting in tools like Looker Studio helps early-stage teams view the whole funnel in one place. Build weekly dashboards for channel performance and monthly cohort views to understand retention and expansion by acquisition source.
Step 6: Scaling and Optimization
Scale only after channels reach acceptable CAC and payback, then expand gradually while watching efficiency.
Reliable scaling uses Net New ARR, payback, and efficiency metrics instead of lead volume alone. Increase budgets first on campaigns with strong contribution margin and payback under about six months.
Next steps for scaling include:
- Expanding audiences through lookalikes, similar keywords, and adjacent segments once core ICP campaigns perform well.
- Adding channels such as Microsoft Ads, targeted communities like Reddit, and partner programs as described in recent SaaS marketing trend analysis.
- Applying advanced tactics such as automated bid rules, time-of-day scheduling, and more granular creative testing.
Growth at this stage usually requires more resources for creative, landing page development, and campaign management, either in-house or with a specialist agency.
Measurement and Validation
Clear success criteria keep teams focused on sustainable pipeline instead of surface-level metrics.
- Primary outcomes: Net New MRR or ARR from marketing, blended CAC, and payback period based on gross margin per customer.
- Pipeline quality: SQL to opportunity rates, ACV by channel, and sales cycle length by source.
- Operational health: Cost per SQL, lead response time, and the share of pipeline generated by marketing versus total quotas.
Establish weekly performance reviews, monthly cohort checks, and quarterly LTV by channel. Use a mix of first-touch, last-touch, and multi-touch views to reduce attribution gaps in complex deals.
Advanced Variations and Extensions
Once the core engine works, advanced strategies can increase volume and efficiency.
- Account-based coverage: Coordinate ads, outbound, and content around defined account lists, using intent signals to prioritize accounts showing buying behavior.
- AI personalization: Use dynamic content and predictive scoring to tailor pages, chat, and offers by industry, company size, and behavior.
- Partner ecosystems: Build referral, integration, and co-marketing programs that become major pipeline sources instead of relying only on direct paid acquisition.
- Content syndication: Use B2B content and intent networks to extend reach and identify accounts researching your space.
Summary and Next Steps
Scalable pipeline for B2B SaaS comes from a connected system across channels, landing pages, nurturing, measurement, and disciplined scaling. The most effective teams set revenue-focused goals, review performance regularly, and scale only after channels prove efficient.
Near-term actions:
- Complete tracking and UTM setup and validate that CRM receives accurate source data.
- Launch focused Google search and LinkedIn campaigns aimed at high-intent and core ICP segments.
- Build or refine dedicated landing pages for main offers and implement basic A/B tests.
- Turn on lead scoring, nurturing sequences, and a weekly revenue-focused performance dashboard.
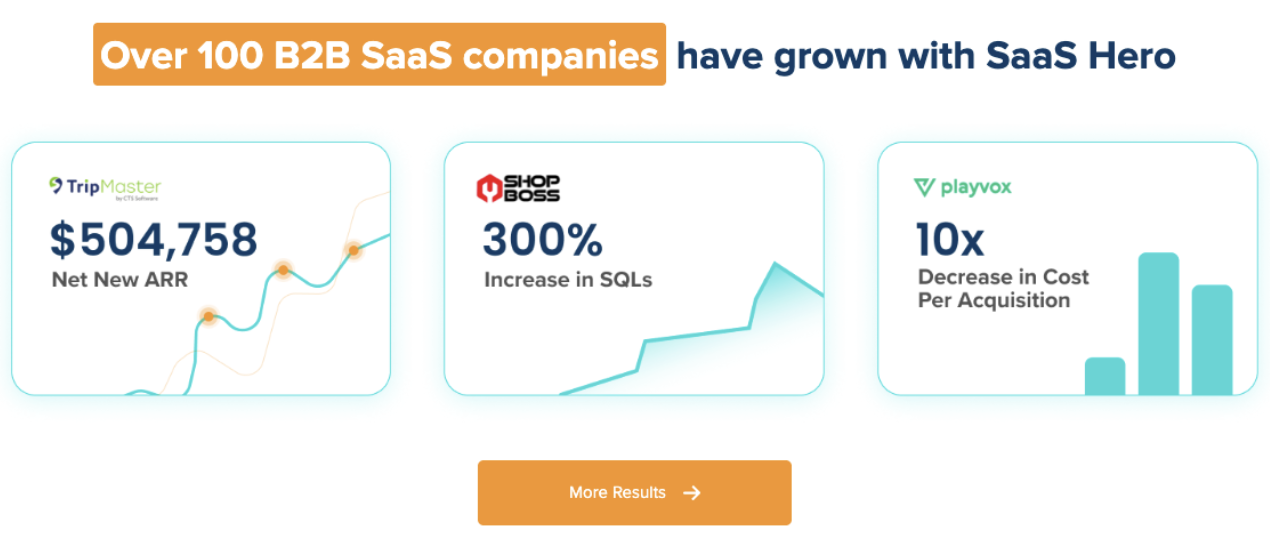
Teams that want hands-on support with channel strategy, landing pages, and revenue reporting can partner with a specialist B2B SaaS agency. You can book a discovery call with SaaSHero to design and implement a complete pipeline generation system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to set up and see results from a scalable pipeline system?
Most teams need 4–6 weeks to complete tracking, landing pages, and first campaigns. Meaningful data usually appears within 2–3 weeks of launch, with solid optimization decisions possible after about 60–90 days and clear revenue impact within 3–6 months, depending on sales cycle length.
Which roles should be involved at each stage?
Tracking and integrations need marketing operations and light engineering support. Channel activation benefits from paid media specialists, while landing pages need copy and design skills. Lead nurturing requires marketing automation ownership, and measurement depends on someone comfortable with analytics and CRM administration.
How should smaller versus larger SaaS companies adapt this framework?
Smaller teams under roughly $1M ARR benefit from focusing on one or two channels such as Google search and simple email nurturing, with lightweight attribution. Companies above $5M ARR can support more complex ABM, multi-channel orchestration, and advanced attribution, usually with specialists in each core area.
What are the main risks and how can they be reduced?
Typical risks include broken tracking, overspending before channels prove efficient, and misalignment on what qualifies as a good lead. Reduce these risks with careful pre-launch testing, conservative early budgets with clear stop rules, and shared MQL and SQL definitions plus regular feedback between marketing and sales.
How often should the pipeline engine be reviewed and updated?
Monitor campaigns daily for technical issues or spend anomalies, review performance and tests weekly, and adjust channel strategy and budgets monthly. Use quarterly reviews to revisit ICP, channel mix, and measurement approaches as the product, market, and sales motion evolve.

